第四章 四、铁器
王志杰
中国在春秋战国和秦汉时期,制铁业兴起并迅速发展,逐渐取代了青铜器用作生产工具、生活用具、武器以至刑具等。铁器极易锈蚀,很难遗存。在陕西省出土的铁器文物中,最早的一件是铁铲,为雍城遗址秦公一号大墓出土,系生产工具。据《陕西省文物志》记载的铁器文物共有13件,其中有7件为茂陵出土文物,十分珍贵。
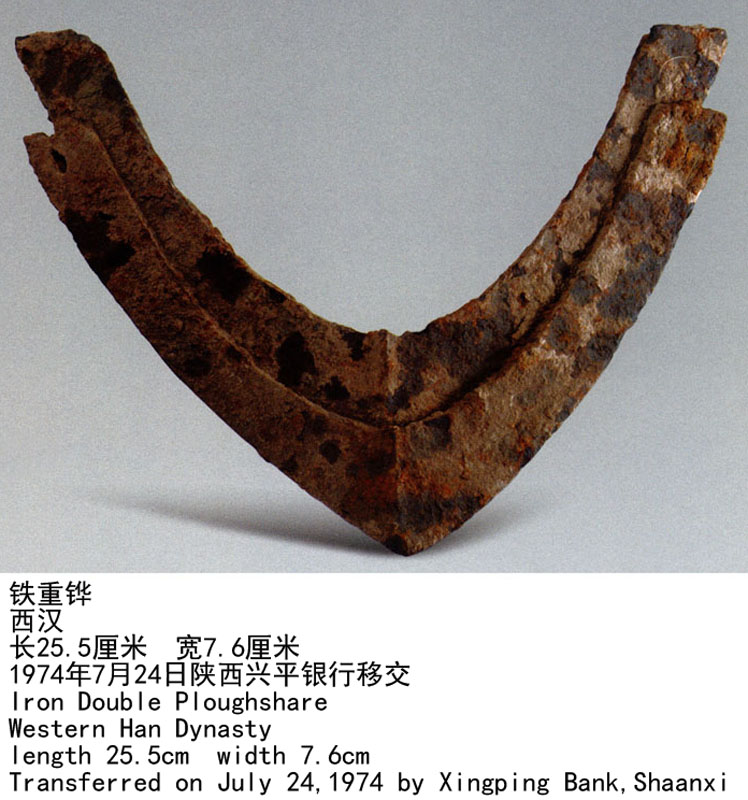
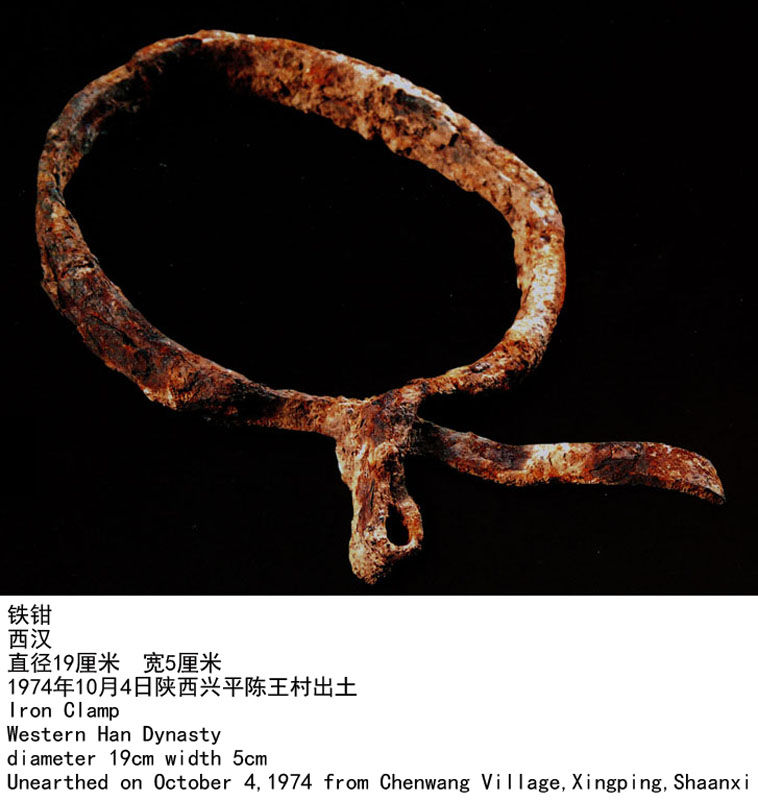
本志所刊出的14件铁器,均为茂陵出土的西汉时期文物。其中大部分是生产工具。有3件铁器为刑具。
这三件铁制刑具,均来源于茂陵的修陵人墓地,距今已有两千多年,位于茂陵园以西约4公里的南位镇陈王村南。
上个世纪70年代,当地群众在平整土地时发现大量戴铁制刑具的骨架,据当时在场的人讲,这些骨架埋葬凌乱,头向不一,有的甚至几具骨架叠压在一起,还有个别为半跪半蹲姿势。陕西省考古研究院汉陵考古队,根据馆藏的这些铁刑具和群众提供的线索,于2007年10月在陈王村南1500米处展开了调查和钻探,在大约4万平方米的范围内发现了数量巨大埋葬密集的小型墓葬。这些墓葬长1.8米—2.0米,宽0.4米—0.6米,深约2.0米—3.0米左右,墓葬间隔0.2米—0.5米,按此密度推算,估计这片墓地埋葬尸骨在2万具以上。因此,可以判定,这就是茂陵修陵造墓人的墓地。
D Iron Wares
Iron industry flourished and developed rapidly in China from the Spring and Autumn Period(770-476 B.C.)and the Warring States Period(475-221 B.C.)to the Han(206 B.C.-220 A.D.)and the Qin(221-206 B.C.)Dynasties.Instead of bronze,iron gradually began use in production,life,weapons and even instruments of torture.Iron wares are likely to be eroded and difficult to be preserved.Discovery of the earliest iron relics unearthed in Shaanxi is an iron spade,which was used as a production tool and excavated from No.1 Grand Tomb of Emperor Qin at the remains site of Yongcheng.Among the 13 pieces of iron relics recorded in the Cultural Relics Data of Shaanxi,seven pieces were unearthed from the Maoling Mausoleum.They possess immense value of research.
The 14 pieces of iron relics listed in this book are all cultural relics unearthed from the Maoling Mausoleum,out of which three pieces were used as instruments of torture and the rest were production tools.
Those three instruments of torture were collected from a graveyard of builders conscripted to construct the Maoling Mausoleum.The graveyard lying 4 kilo's west to the Maoling Mausoleum Area dates back to 2000 years ago.
In the 70's of the last century,the local people,leveling the land,discovered lots of skeletons in iron fetters,which were disarrayed in a mess,even piled up.A few individuals were found kneeling or squatting.
Based on the iron instruments of torture collected by the museum and clues provided by the local people,an archaeological team from Shaanxi Archaeological Academy conducted an investigation by drilling an area of 40000 square meters south to Chenwang Village in October,2007.There,they found huge numbers of small tombs,which measures 1.8m-2.0m long,0.4m-0.6m wide and 2.0m-3.0m deep,in separation of 0.2m-0.5m between them.In calculation of such density,the graveyard is estimated to have buried over 20000 corpses.Judging from that,the graveyard was for mausoleum builders.













茂陵文物鉴赏图志/王志杰著.—西安:三秦出版社,2012.