您现在的位置:首页 > 研究论著 > 汉阳陵·比萨:文化遗产的原址保护与考古博
汉阳陵地下博物馆遗址区域环境状况分析
李库(汉阳陵博物馆)
汉阳陵地下博物馆即帝陵外藏坑保护展示厅是一座全新的遗址类博物馆,博物馆建筑基本全埋于地下,建筑顶部覆土种草绿化,陵园历史环境不受影响。建筑修建在外藏坑坑体上,外藏坑被特殊的玻璃合围起来,与观光者隔离,遗址区域相对封闭,这样既利于文物遗址的保存,又让游客透过玻璃近距离地观赏到遗址,有身临其境的震撼,这是一种全新的保护展示理念。遗址区域封闭之后,期间的环境直接影响着文化遗存的寿命。通过近三年的观察和跟踪检测,遗址区域环境已经趋于稳定和平衡,较为稳定的环境对于文物遗址的长久保存是非常有利的。
一、帝陵外藏坑的考古钻探和发掘
1998年,汉阳陵帝陵园考古勘探取得突破性进展,陵园四面墓道钻探发现之后,陵园钻探工作继续进行,钻探人员手持探铲,最长的探铲长度达到了近12米,迎着烈日、冒着酷暑,穿梭于果树林和庄稼田里,功夫不负有心人,经过近乎1年的勘探,陵园内围绕封土四周81座外藏坑已经探明。根据钻探结果,陵园东侧13号坑埋葬品密集,探铲在此处打上了许多陶质文物,带上来陶质有的还有彩绘,非常吸引人。于是经过上报有关部门,陕西省考古研究所阳陵考古队开始在13号坑东端布置探沟1条,进行发掘。在发掘长22米的区域内出土陶狗、陶绵羊、陶山羊、陶猪等陶塑动物1000余件,上下两层摆放,密密匝匝。陶狗有灰色、白色、黄色等,陶猪以黑色和白色为主,羊以灰色为主,有的羊身上残留朱红色彩绘痕迹,钻探时留下的探孔在动物的身上显现了出来。
13号坑试掘部分埋藏丰富更激发了考古人员的热情,同时也引起了上级领导的高度重视,加上陕西省委、省政府决定开发建设汉文化旅游景区的重大决策,于是13号坑的考古工作面积不断加大,并逐步延伸至陵东11—21号坑的全面发掘。帝陵封土东侧编号为DK11—21的11个外藏坑地科学发掘,出土了大量的包括文吏、武士、男女侍从、宦者等各种身份的陶俑,羊、猪、狗、鸡等各类陶塑家畜,原大或缩小为三分之一的木车马,各种质地的生活器具和兵器以及粮食、肉类、纺织品等生活消费品,可谓种类齐全,洋洋大观。尤其是坑内出土的“宗正之印”、“大官之印”、“永巷丞印”、“内官丞印”、“宦者丞印”、“东织令印”等有文字的印章、封泥,足以证实这里代表和象征的是“卫尉”、“宗正”、“少府”三卿或者其下属的官署机构,我们相信随着以后帝陵81座外藏坑的发掘,其它六卿机构的印章或者封泥等文字资料也将随之出土面世,从而证实81座外藏坑象征着当时西汉王朝中央官署的“九卿”机构。这些机构分别为皇帝准备了丰富的随葬品,并由主管陵园建设的官员依照一定的顺序建设外藏坑埋藏于皇帝的棺椁四周,犹如皇帝生前当朝一般。
二、地下博物馆的设计和建设
1998年—1999年伴随着汉阳陵考古成果的不断深入、2894亩文物保护用地的征用以及考古陈列馆暨帝陵外藏坑考古发掘现场的对外开放,在帝陵外藏坑处建设展示厅已经迫在眉睫了。2000年3月,地下博物馆设计工作开始启动,前后历时3年多,2003年7月方案最终确定,最后的设计主要由西安建筑科技大学文化遗产保护研究中心和台湾李祖原建筑事务所完成。初步设计和施工图设计由西安建筑科技大学文化遗产保护研究中心与设计研究院、台湾李祖原建筑事务所、中国文物研究所、陕西省古建研究所、日本东京照明株式会社、西安通力电子公司以及日本、斯洛文尼亚的有关专家合作共同完成。
经过1年多时间的准备,2004年8月,帝陵外藏坑保护展示厅破土动工了,这是关心汉阳陵发展建设和在汉阳陵工作的每一个职工激动人心的时刻,也是汉阳陵博物馆建设划时代的里程碑。10座外藏坑全面回填保护,灰桩试验、预应力梁的浇注等工程逐一开展。特别是2005年下半年开始,土建、装修、玻璃安装、陈列布展、灯光、安防等诸多工作全面开展,为了不影响工期,按时开馆,许多工作交叉作业,昼夜进行,夜以继日。
经过各方面的努力,2006年3月31日帝陵外藏坑保护展示厅建成开放了。
三、环境状况跟踪监测
帝陵外藏坑从1998年开始发掘,到2004年全面回填,再到2006年初封闭之后二次发掘重新对外开放,所处环境接连发生较大的改变,这样的改变对于遗址的保存是非常不利的,势必造成文物和遗址的某些病变。基于这种因素的考虑,2006年开馆伊始,汉阳陵博物馆即可联合西安文物保护修复中心、中科院地球环境研究所等单位一起对封闭区环境进行跟踪监测,重点调查遗址区空气温湿度的变化,并定期检测了空气中的有害气体和颗粒物、微生物及霉菌活动的情况,同时进行封闭空间内土壤含水量、可溶盐的分析测定,为了解封闭遗址区域的环境状况提供了详实、可靠、科学的第一手数据依据。
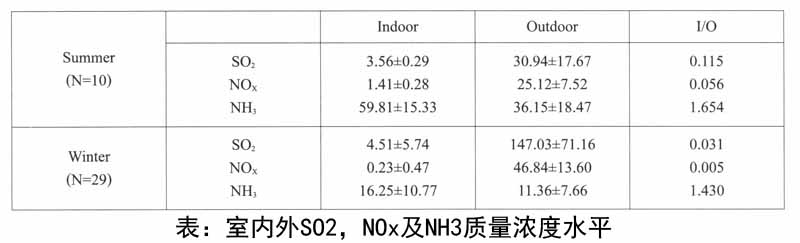
此次我们仅通过环境数据的变化、对比分析,确定目前遗址区域内的环境状况,环境数据主要包括温湿度变化,大气中的SO2、NOX及NOX3的浓度水平,并通过馆内外大气中黑碳粒子的变化了解玻璃封闭对于大气中颗粒物的隔挡情况。
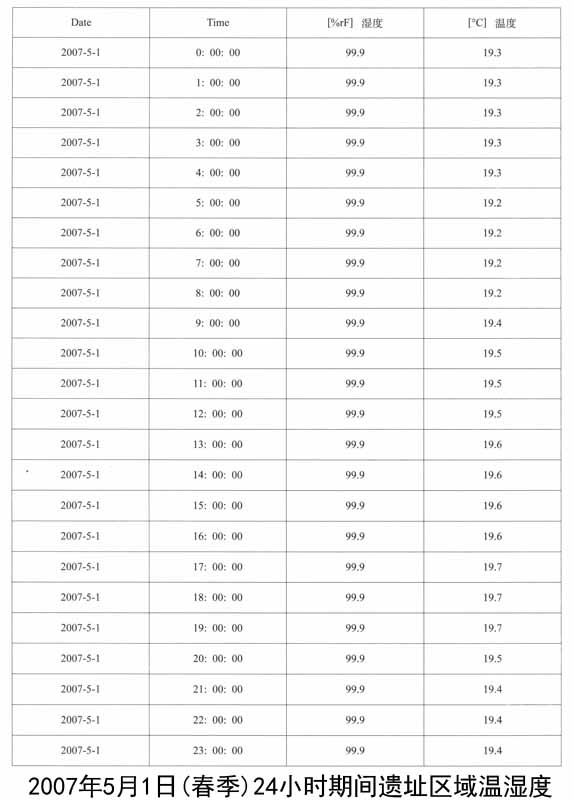
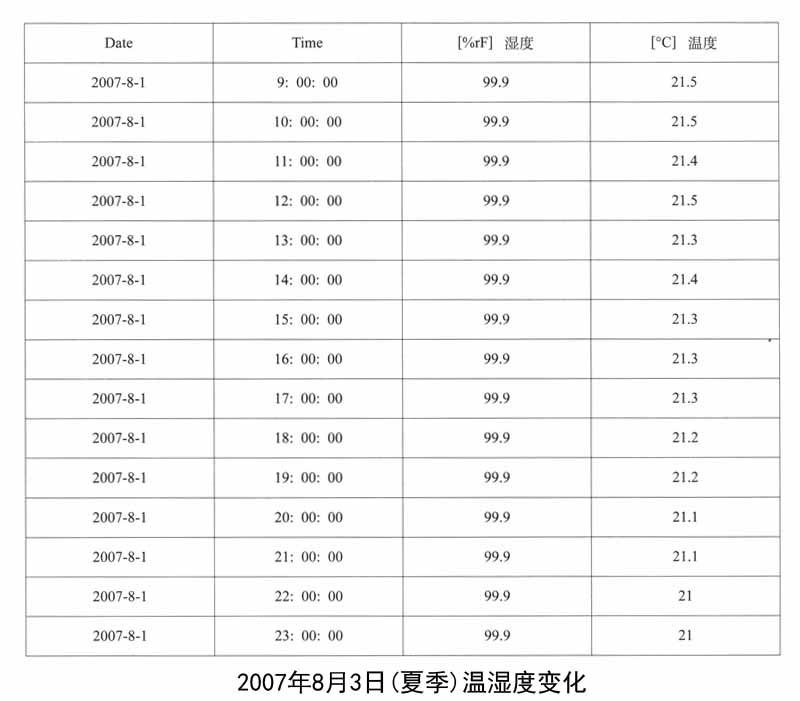
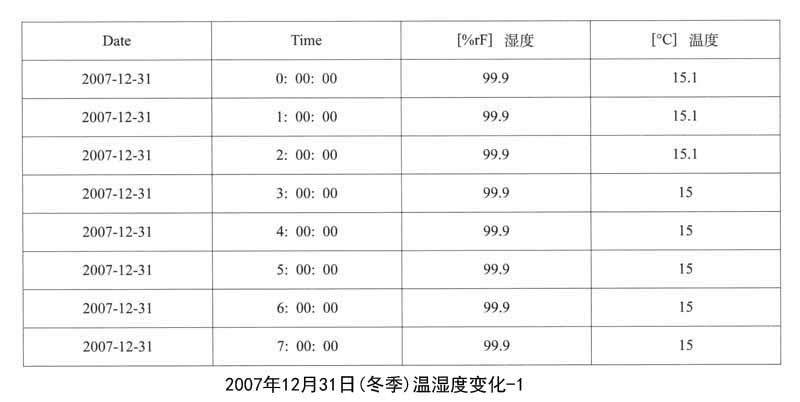
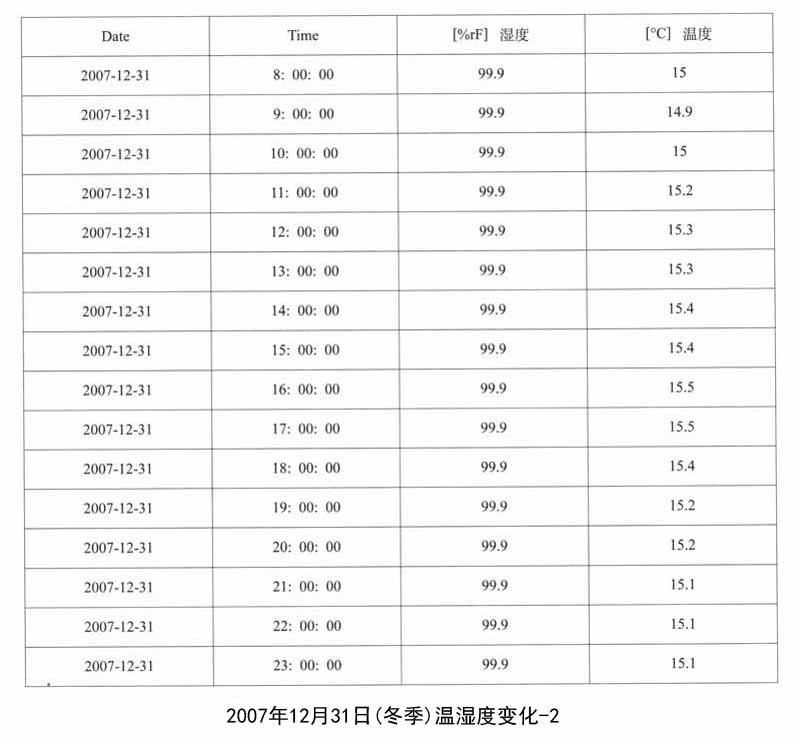
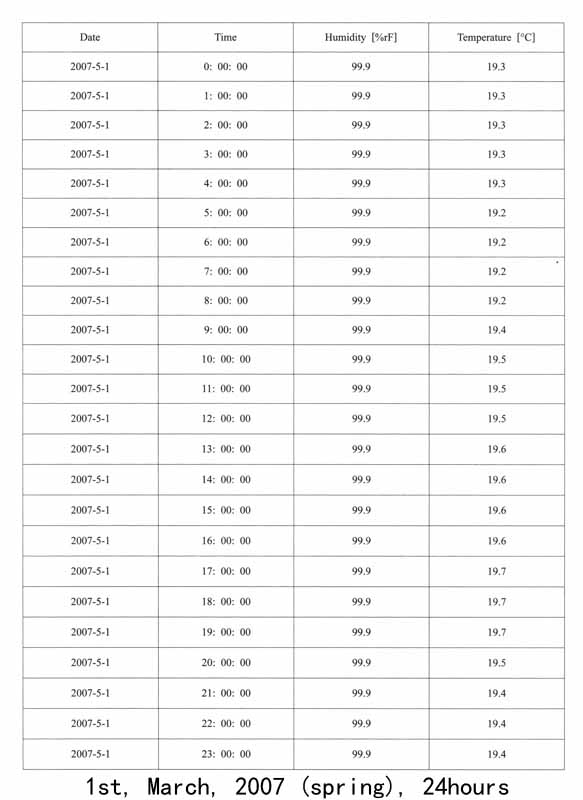
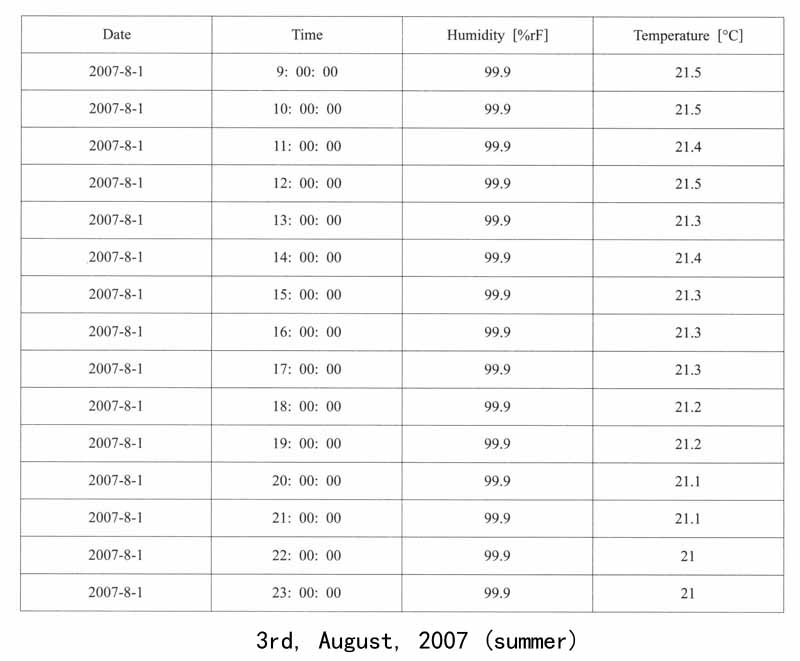
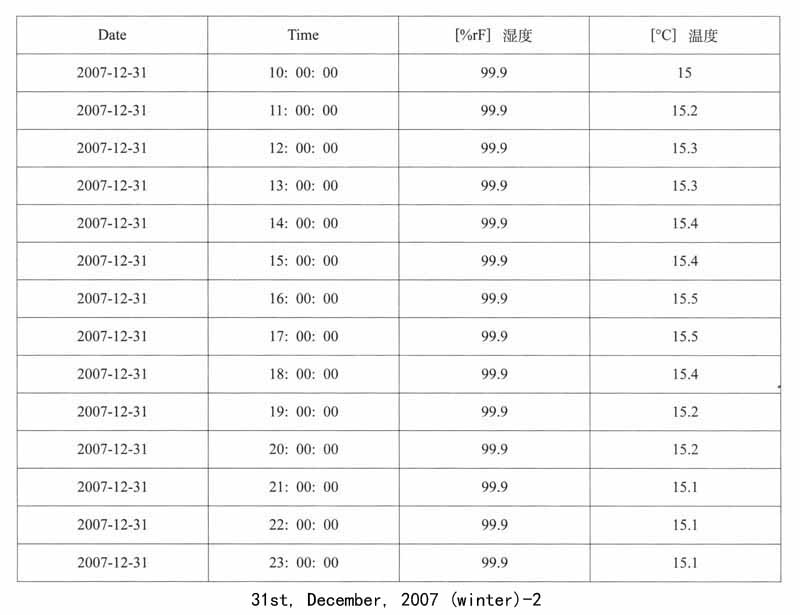
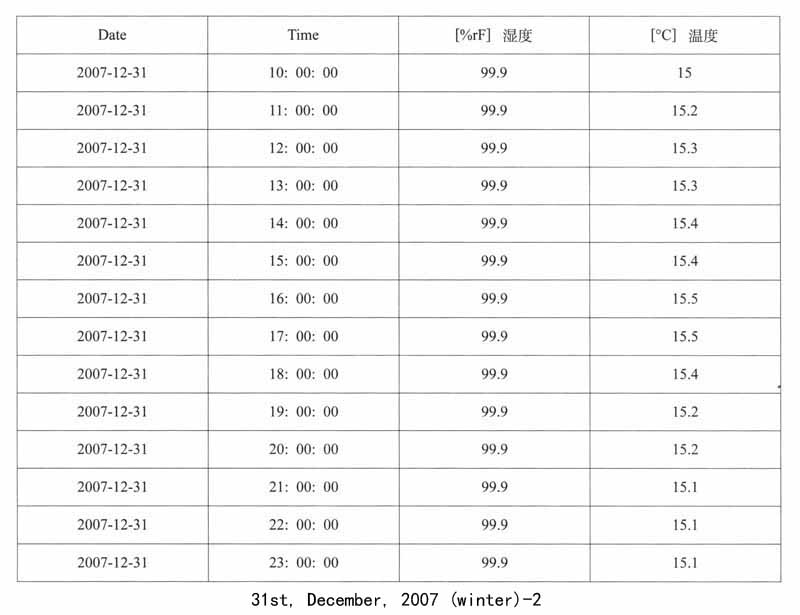
1.遗址区空气温湿度变化的监测:遗址区域放置温湿度自动记录仪,设定每小时自动记录一次,定期采集数据。以下列出其中2007年5月1日、8月3日、12月31日三天的记录数据,表现空气温湿度的日变化和年变化。
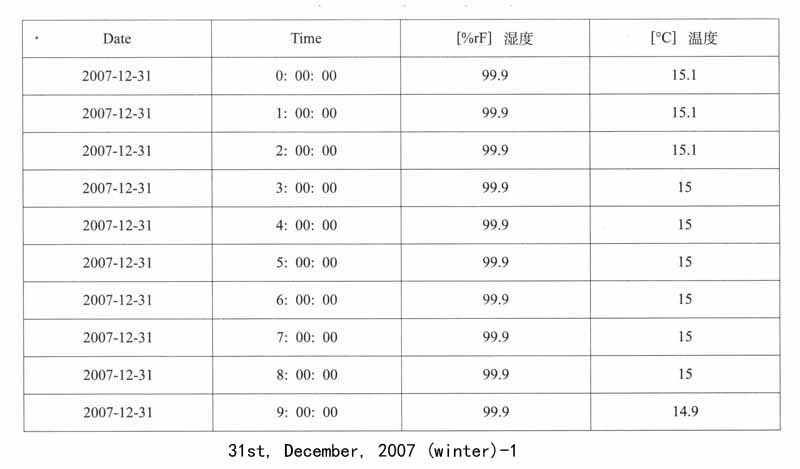
馆外的气象状况与馆内遗址保存环境条件的对比,能够直接反映出地下博物馆建设对于遗址保存所带来的优点,这里笔者列举了2007年冬季馆外气象状况,这些数据与馆内同时期温湿度的监测数据可以证明遗址区域的环境得到了相对地控制,温湿度已经趋于稳定。
馆外温度的日均值为0.4±2.7℃,介于﹣4.9℃-3.8℃;相对湿度的日均值为68.7±20.7%,介于29.3%-93.9%之间。在本研究冬季采样期内,前期以阴天和多云天气为主,从08年1月10日到17日,均为下雪天,有一段明显的降温过程。温度和相对湿度呈现出相反的趋势,且变化幅度较大。
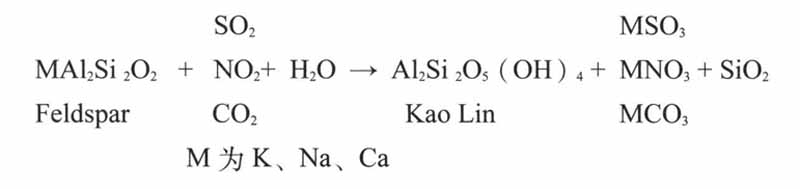
2.馆内外大气中SO2,NOX及NH3的浓度水平:大气中SO2,NOX及NH3气体对于文物遗址的保存是有害的,SO2,NOX在与水的条件下,会发生下列化学反应:
这种反应导致陶器内部、特别是表面结构发生变化,强度下降,易碎,甚至表面酥解、粉化。
文物保存区域中有害气体的含量(浓度水平)是衡量保存环境优良状态的重要指标,此次通过在馆内外同时安装大气采样器,采集气体,分析有害气体含量。
Unit:μg/m3
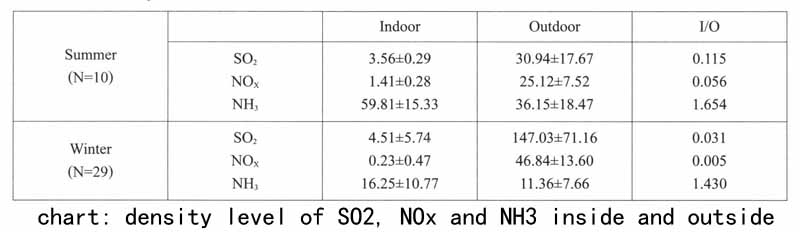
上表是冬夏两个采样季期间地下博物馆室内外SO2,NOX及NH3,质量浓度水平,它们的变化特征:
(1)SO2
夏季室外大气中SO2的平均浓度为30.94μgm-3,而展厅中SO2为3.56μgm-3,室外为室内浓度的约8.7倍。冬季室外大气中SO2的平均浓度达到147.Oμgm-3,展厅SO2约为4.5μgm-3,室外为室内浓度的约32倍。室内浓度基本符合国际文物组织制定的二氧化硫浓度标准(10μgm-3),冬季有个别天浓度超标。室内SO2浓度在冬夏季比较接近,处于3-4gm-3的浓度水平,而室外SO2相差较远,冬季平均浓度是夏季平均浓度的4倍,这可能主要与冬季SO2排放量增加有关,博物馆附近的渭河发电厂可能是其主要来源。
(2)NOX
夏季室外大气中NOX的平均浓度为25.1gm-3,而展厅中的NOX为1.41gm-3,室外为室内浓度的约18.5倍。冬季室外大气中NOX的平均浓度达到46.8gm-3,展厅的NOX约为0.2gm-3,室外为室内浓度的约234倍。对比测量数据可知,室内NOX浓度在冬夏季比较接近,处于1gm-3的浓度水平,而室外NOX浓度也存在一定差别,冬季平均浓度比夏季平均浓度高21.7gm-3,这可能主要与冬季NOX排放量增加有关。冬夏季室内NOX浓度均较低,明显低于国际文物组织制定的二氧化氮浓度标准(10μgm-3),表明NOX气体在展厅中不是主要的污染气体。
(3)NH3
夏季室外大气中NH3的平均浓度为36.15mgm-3,而展厅中NH3为59.81μgm-3,室内高于室外浓度,约为1.65倍。冬季室外大气中NH3的平均浓度达到11.36μgm-3,展厅中NH3约为16.25μgm-3,室内为室外浓度的约1.4倍。由于大气中氨气主要来源为人为和农田排放贡献的,室外大气中NH3应主要来自博物馆周边的农田如化肥分解产生的气体,室内NH3除受室外大气NH3渗入外,游客排放的NH3应该是导致室内浓度高于室外浓度的主要原因。冬季由于气温较低(0℃左右),农田中氨气的排放不活跃,这是冬季大气NH3偏低的主要原因。夏季室外平均NH3浓度是冬季室外的3.18倍,而夏季室内平均NH3是冬季室内平均浓度的3.68倍,因此室内浓度的冬夏季节差异大于室外,这可能主要与夏季地下博物馆有较多的游客流量,以及夏季温度高导致游客汗液排放而产生NH3。
3.大气中颗粒物质的变化特征:
此次监测是以内外两个环境的大气中黑碳粒子的含量来判断玻璃封闭的效果的。当用热学分析方法来区别碳气溶胶中的有机和无机组分时,有强烈吸光特性的这部分含碳物质被称为黑碳(BC),它不溶于任何极性和非极性溶剂,在350℃以下的纯氧环境中是稳定的,不会发生任何化学反应。故在空气污染研究中通常被用作示踪物。在冬季采样中,采用两台黑碳测量仪(Aethalometer)同步测量了大气BC的浓度变化。
基于每5分钟测量数据基础上的小时浓度日变化图,由图可以看出,室外浓度明显高于室内浓度,室外BC浓度平均为13.5μgm-3,室内浓度平均为4.4μgm-3,室外浓度为室内浓度的约3倍,这可能指示了细颗粒物的变化情况,即室外颗粒物是室内颗粒物浓度的约3倍。这进一步表明玻璃展室并不能完全隔绝室内外的空气污染物的交换。
室内外BC的日变化趋势也存在一定差别,室外BC的日内变化基本与西安的变化相似,室内的最高值和最低值分别出现在12点和23点。室外BC的变化趋势表明其BC浓度受控于污染源排放和空气稀释状况,而室内BC可能主要是反映了室外BC对室内渗入,在展厅内具有一定的累计效应,在中午前后达到最大值,然后减少,在午夜时由于交换的隔绝程度高,故其浓度衰减至最低值。
四、环境状况分析
通过一系列的监测和分析,地下博物馆遗址区域环境状况已经基本掌握。博物馆的建设和玻璃的封闭,减少了遗址区域与外界环境的直接交流,大气交换减慢。封闭空间环境优于馆外,温湿度趋于平稳,昼夜温度变化在1℃之内,年温度变化最大不超过10℃,空气相对湿度接近饱和状态,且基本稳定,土遗址风化干裂等现象得到控制。大气中的有害气体和颗粒物大量减少,二氧化硫、氮氧化物的浓度馆外高出馆内10倍,甚至数十倍,大气中黑碳粒子的含量减少至1/3左右。有害气体含量明显低于国际文物组织制定的浓度标准,这些对于文物遗址的保存是有利的。
汉阳陵地下博物馆遗址厅,对于保持储存文物环境的温湿度的相对恒定有较为明显的作用。短期内馆内的温湿度在一定范围内可以达到一个相对稳定的状态,但是从两个季节的比较可以看出,馆内的温湿度在一定程度上仍然受室外和人为活动的影响,呈现出温度的夏高、冬低的变化趋势。因此对于温度的控制,仍然是一个首要的问题。就两个季节比较而言,夏季遗址厅内的微环境稳定性更高,这可能与夏季长时间使用空调有关。
结束语:文物所处环境除了本文涉及到的大气温湿度,大气中的有害气体、颗粒物质之外,埋藏文物的土壤、土壤中的水以及这种环境条件下霉菌滋生、繁衍的情况等也是非常重要的部分,这些工作正在完成阶段,以后将逐步成文公布。
Analysis on Han Yangling Underground Museum Environments
Li Ku (Hah Yangling Museum)
Han Yangling Underground Museum(HYUM) is a new type of on-the-site museum,which was basically built underground with green plantation on its top.The major construction was built on the original pits,and protects by special glass wall,which separates the visitors and the archeological site into two dif-ferent environments. This technique provides brand new concept of on-the-spot protection and exhibition.Actually,inside the closed archeological site,environments are very essential to the site duration. After 3 years of investigation and monitoring,we found the environment of archeological site has been in a con-siderably stable condition,which is beneficial for cultural heritage protection.
1. Archeological excavation on secondary burial pits
In 1998,the archeological excavation works of Han Yanling Mausoleum Complex(HYMC) had a breakthrough.After finding the four tomb passages around the emperor's tomb,the archeologists continued work under the scorching sunshine with shovels in hand,after a year's hardworking,81 secondary burial pits around the Emperor's tomb were discovered. Drilling results show that No.13 pits in the east side of Emperor's mausoleum are filled with burial objects,most of them are pottery relics,some even attached with bright paintings.After getting approval from the superior management bureau,an archaeological team subordinate to Shaanxi Provincial Cultural Heritage Bureau was set up to do the excavation works. From this 22m long pit—east part of No.13,they excavated more than 1000 pottery animals inlaid in two layers,including dogs,sheep,goats,pigs and so on. The pottery dogs are grey,white and yellow in color;pottery pigs are mainly black and white;the pottery goats are grey,but some left with vermilion pigment traces.The drilling holes can be clearly seen on the animal's body.
This pilot excavation of No.13 pit attracted people's interests and enthusiasm,as well as the great at-tention of superior organizations.The Shaanxi Provincial Government even decided to establish a scenic spot based on Han cultural here. Correspondingly the excavation areas on No.13 have been enlarged to 11 pits,from No. 11 to No.21 to the eastern side of the Emperor's mausoleum.Excavation fruits from these 10 pits include massive pottery figures such as officials,warriors,male and female retinues,eunuchs,do-mestic pottery animals(sheep,pigs,dogs,chickens),miniature wooden chariots,daily utensils,weapons,grains,meat,textiles etc. The most unique among them are a variety of official seals,including“Zong-Zheng-Zhi-Yin”(official in charge of royal kinsmen),“Da-Guan-Zhi-Yin”(royal chef),“Yong-Xiang-Cheng-Yin” (official in charge of detained concubines),“Huan-Zhe-Cheng-Yin”(eunuch),“Dong-Zhi-Ling-Yin”(official in charge of textile affairs).These seals are the representatives of different depart-ments affiliated to central government. We believed if all 81 pits were excavated,we could find a complete establishment of central government in the Western Han dynasty.Every department contains a lot of burial things for the Emperor,which would have been buried in strict hierarchy sequence around the mound by builders,representing real life activities.
2. Construction and Design of Underground Museum
With the deepening of archaeological fruits in HYMC from 1998 to 1999,the requisition of 2849 acres of land for heritage conservation and the opening of the Archeological Exhibition Hall and the archeological excavation site of secondary burial pits,the establishment of a new Underground Museum is in great need.In March 2000,the planning works of underground museum was staged,3 years later in July,2003,the scheme designed by Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology,Cultural Heritage Conservation Centre and C. Y. LEE&PARTNERS Architects&Planners was chosen as a final one. The draft design and project drawings were jointly made by Xian University of Architecture and Technology Cultural Heritage Conserva-tion Centre and Design Centre; C.Y.LEE&PARTNERS Architects&Planners;CNICP;Shaanxi Provincial Architecture Research Institute;Lighting co.,ltd.Tokyo,Japan;Xian Tong Li electronics,and other experts from Japan and Slovenia.
After more than a year preparation works,Han Yangling Underground Museum project was officially started in August,2004.This is one of the most important moments for every people who are concerned about HYUM,also an epoch-making construction.The refilling of 10 pits for protection,engineering test,pre-stressed beam placing program were implemented in steps.Especially in the latter half of 2005,such works as construction,decoration,glass installation,exhibition,lighting,security were launched com-prehensively.To ensure that the museum opened on time,many works were done simultaneously and round the clock.
After all these efforts,on 31st,March,2006,the Underground Museum was opened finally.
3. Environmental Monitoring
The excavation of burial pits of Emperor's mausoleum was started in 1998,in 2004,all pits were refilled for construction of the museum,and in 2006 after the construction of the underground museum was completed,the second excavation was done.The environment has experienced so many changes,which is harmful for the protection of the site,the relics and site have pathologically changed.Based on such con-siderations,in the beginning of 2006,Han Yangling museum combined with Xian Cultural Heritage Res-toration Centre,Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Earth Enviromnent among others have monitored and tested the environments in the closed atmosphere,especially air temperature and humidity changes on site,and the regular minitor have been done towards pernicious gases,particulate matters,microorganisms and mould activities. At the same time,analyses on soil moisture and soluble salts have been done to provide detailed,reliable,first-hand scientific data of the environmental conditions in the closed site.
At present,through the comparative analysis on environmental data changes,we are clear about the on-the-site environment situations,including major temperature and humidity changes,atmosphere density level of SO2,NOX and NH3,and understand the blockage situations of atmosphere particulate matters in the glass-sealed environment through comparing the changes of black air carbon particles inside and outside the museum.
①. Monitoring the temperature and humidity changes on the site:In the site area,automatic temperature and humidity recorders are placed,collecting records every hour automatically.The following list recorded the data in the 1st,March,2007,the 3rd,August,2007 and the 31st,December,2007 shows the daily and yearly changes of the site.
By comparison the meteorological conditions outside an inside the museum,the advantages of site pro-tection brought by the underground museum can be proved.The author also lists meteorological conditions outside the museum in winter,and these data together with temperature and humidity changes date,could prove that the environments in the site have been relatively controlled with temperature and humidity ap-proach to stabilization.
Atmosphere temperature,relative humidity and wind speed
(07.12.20-08.1.17)
The daily average temperature outside museum is 0.4±2.7℃,between -4.9℃-3.8℃ and relative daily average humidity is 68.7±20.7℃,between 29.3%-93.9%. During the winter period of sample-collecting,the early days were mainly cloudy,while from 10th to 17th,January,2007,it snowed,as the temperature declining can be clearly seen in the chart.The temperature and relative humidity show a different trend,and the scope of change is relatively great.
②Atmosphere density level of SO2,NOX and NH3 inside and outside the museum:
The SO2,NOX and NH3 in air are harmful to site protection,SO2 and NOX in the water condition could have the following chemical reaction:
This reaction could lead to internal,especially surface structure changes of the pottery,like intensity decrease,breakable,even crisp and dusting changes on the surface.
The pernicious gases (density level) on protection site,is an important indicator of the state of the environmental preservation.Now through installing Atmosphere Sampling Machine,the collection of gas-samples and the analysis of pernicious gases can be realized.
chart: density level of SO2,NOx and NH3 inside and outside
The data of above chart were collected both in winter and summer,and their changes go as follows:
1) SO2
In summer,the atmosphere SO2 density average level is 30.94μgm-3,and SO2 density level in exhibition hall is 3.56μgm-3.The outdoor density level is 7.8 times higher than that indoors.In winter,the indoor SO2 density average level is 147.0μgm-3,and SO2 density level is 4.5μgm-3,while the outdoor density av-erage level is 32 times higher than that indoors.The indoor density can basically meet the SO2 level standard (10μgm-3) designated by International Cultural Organizations,with only a few disqualified days during win-ter. The indoor SO2 density level is almost the same in winter and summer,maintaining within 3-4μgm-3,while the outdoor exceeds the standard by a large margin.The density level in winter is 4 times higher than that in summer,which maybe the result of SO2 emission and location of the museum,which is adjacent to the Wei He River Power plant.
2) NOx
In summer,the indoor atmosphere NOx density average level is 25.1μgm-3,and NOx density level is 1.41μgm-3,while the outdoor density level is 18.5 times higher than that indoors.In winter,the indoor atmosphere NOx density average level is 46.8μgm-3,and NOx density level is 0.2μgm-3,while the outdoor density level is 234 times higher than that indoors.By comparison the data,we can conclude that the indoor NOx density level is closer in winter and summer,staying in the level of 1 μgm-3,while there are differences in outdoor situation,the NOx density average level in winter is 21.7μgm-3 higher than that in summer,which maybe the result of the increased NOx emission level in winter.In winter and summer,the indoor NOx density level is considerably low,obviously lower than the standard 10μgm-3 NOx density level stipulated by international heritage organization,indicating that NOx is not the main polluting gases in the museum.
3) NH3
In summer,the outdoor NH3 density average level is 36.15μgm-3,and the indoor NH3 density level is 59.81μgm-3,the indoor level is about 1.65 times higher than that outdoors.In winter,the outdoor NH3 density average level is 11.36μgm-3,and the indoor NH3 density level is 16.25μgm-3,the outdoor density level is 1.4 times higher than indoor one. The main sources of NH3 in the air are possible come from mad-made agricultural emission,and outdoor NH3 is mainly due to the fertilizer decomposition at Surrounding farmlands.In addition to the outdoor NH3 infiltration,indoor NH3 average level also influenced by visitors' NH3 emission,which should be the major reason that the indoor NH3 density level is higher than outdoor one.
③Variable characteristics of atmospheric particulate matters
This monitoring is based on the quantity of atmospheric black carbon particles both indoors and out-doors to determine the effect of glass-enclosed environment. When we chose the thermal analysis methods to separate carbonaceous aerosol's organic from inorganic parts,those carbon matters with strong light ab-sorption characteristics are called black carbon(BC),which does not dissolved in any polar or non-polar solvents and is stable in below 350℃ pure oxygen conditions without any chemical reactions occured.So,the BC matters are usually taken as the trace symbol in pollution research. In the winter,we use two Aethal-ometer machines to measure atmospheric BC density level changes.
Based on per hour density changes measured in every 5mins,we can conclude from the table,outdoor density level is obviously 3 times higher than that indoor,with outdoor BC density averaging 13.5μgm-3,and indoor's 4.4μgm-3.This information indicates that particle matter changes,or outdoor particle matter density is 3 times higher than that indoors,and the air pollutant exchanges inside and outside sealed classes could not be totally prohibited.
Actually differences still exist between indoor and outdoor daily BC changes,basically the outdoor changes are close to Xi'an City,while the indoor maximum and minimum point stay at 12°and 23°respec-tively.The outdoor BC changing trend indicates that it is influenced both by pollution resources emission and air dilution,while the indoor BC possibly come from outside,having some cumulative effects in the museum,and it reaches maximum point at noon,then decrease,minimum density appears in midnight due to high level isolation.
4. Environmental Analysis
Through systemic monitoring and analysis we basically learn about the environmental conditions in the underground museum. The construction of museum and glass-sealed methods reduce the direct exchange between inside and outside atmosphere,slowing down the air exchanges.A closed environment is better than the open one,because the temperature and humidity are stabile,temperature changes between day and night maintaining within 1℃,and annual changes stay around 10℃;atmosphere humidity is basically stable and close to saturation;the air-drying phenomena of earthen heritage have been under control;a clear reduction in pernicious gases and particle matters;SO2 and NOx density level are more than 10 times higher than that outdoors;the atmospheric black carbon particles quantity reduced to about 1/3.The pernicious gases level is absolutely lower then density standard made by International Cultural Organizations,which are beneficial for cultural heritage protection.
HYUM plays a significant role in maintaining environmental temperature and humidity. In short terms,the inside temperature and humidity could reach a relatively stable state to some extent; however,comparison between two seasons shows that the indoor temperature and humidity could be influenced by people's activi-ties and outdoor environments to some degree,being higher in summer and lower in winter.Therefore,the temperature control is still an important problem.In the terms of the comparison between two seasons,in summer times,small environment on site might be more stable due to the function of air-conditioners.
Conclusion:the cultural relics'environments include not only the atmosphere,pernicious gases,particle matters,burial earth and soil moisture mentioned in this article,but also the mould breeding and propagation,which are under monitoring and will be released later.

汉阳陵·比萨:文化遗产的原址保护与考古博物馆